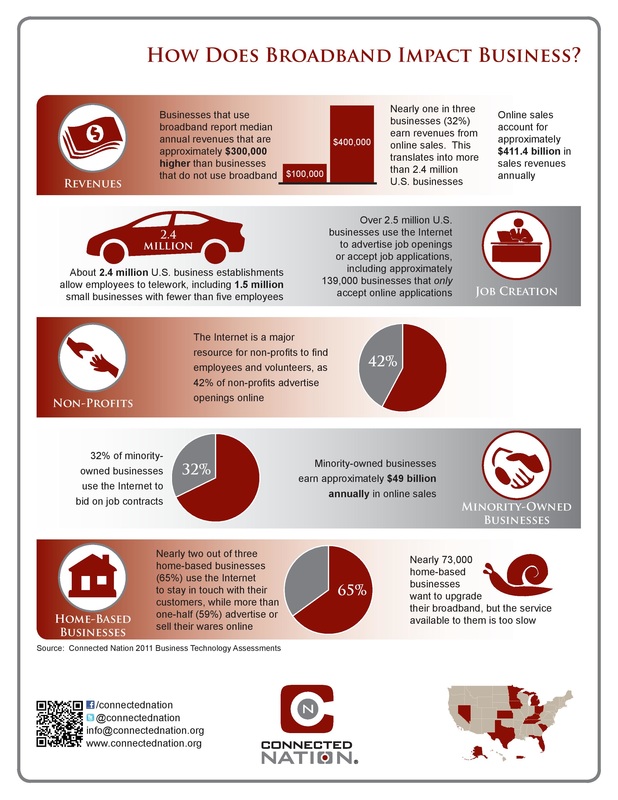
|
"The economic future of communities in Iowa depends not only upon whether robust broadband infrastructure is present but also upon whether businesses and individuals fully utilize that technology to grow and develop local economies."
Connect Iowa Today's economy is more dependent than ever on reliable broadband service.From small businesses to the largest industries, broadband is vital to economic growth in 21st century communities. If access to broadband is limited, so will be the opportunities for businesses to grow and add jobs.
The connection between quality broadband and the local economy is clear.
"High speed broadband complements other attributes of a great community, such as great health care, low cost of living and recreation opportunities." National League of Cities, "Who Needs A Gig?"
"In today's global economy, it is important to have the resources and technology needed to have a competitive advantage. Quality high-speed Internet service is not only an integral component in any business but it also spurs job creation and innovation." former Iowa Governor Terry Branstad. "And in the 21st century, in this age of innovation and in technology, so much of the prosperity that we’re striving for, so many of the jobs that we want to create depend on our digital economy. It depends on our ability to connect, and to shop, and to do business, and discover and learn online, in cyberspace." President Barack Obama, remarks at Cedar Falls Utilities, January 2015. "Municipal networks create jobs by ensuring businesses have fast, affordable, and reliable Internet access; the old DSL and cable networks just don't cut it." Institute for Local Self Reliance. "Businesses, regardless of size or location, can use broadband technology to sell to customers around the country and the world." U.S Chamber of Commerce Broadband Matters for Jobs and
|
|
|
From the Council of Economic Advisors, "Strengthening the Rural Economy-Strengthening Rural Infrastructure"
There are several reasons that expanded broadband service is important for employment and income growth in rural areas. Most employment growth in the United States over the last several decades has been in the service sector, where jobs are particularly likely to benefit from broadband access. Broadband service may allow rural areas to compete for a range of service jobs, from call centers to software development. And even in non-service industries, internet tools can help businesses connect more efficiently with customers and suppliers. For instance, American farmers can use the internet to track product prices, obtain weather forecasts, buy and sell commodity futures, track the progress of supplies ordered or products shipped, and find markets for specialty farm products. Broadband internet connections also are increasingly useful as a substitute for business travel.
Broadband-enabled employment is valuable in rural areas not only for the income opportunities it provides, but also because it helps further diversify local economies. Broadband internet access enables employment that is both flexible and untethered to local economic conditions. One example of how broadband access can diversify income sources is through home businesses, which are substantially more common in rural areas than urban ones. Broadband service helps rural businesses find markets that otherwise might be unavailable to them, facilitates online ordering and billing, and integrates the rural economy with the rest of the country (and the world) more effectively than is possible over slow-speed internet connections. It also allows continued access to online training and education.
There are several reasons that expanded broadband service is important for employment and income growth in rural areas. Most employment growth in the United States over the last several decades has been in the service sector, where jobs are particularly likely to benefit from broadband access. Broadband service may allow rural areas to compete for a range of service jobs, from call centers to software development. And even in non-service industries, internet tools can help businesses connect more efficiently with customers and suppliers. For instance, American farmers can use the internet to track product prices, obtain weather forecasts, buy and sell commodity futures, track the progress of supplies ordered or products shipped, and find markets for specialty farm products. Broadband internet connections also are increasingly useful as a substitute for business travel.
Broadband-enabled employment is valuable in rural areas not only for the income opportunities it provides, but also because it helps further diversify local economies. Broadband internet access enables employment that is both flexible and untethered to local economic conditions. One example of how broadband access can diversify income sources is through home businesses, which are substantially more common in rural areas than urban ones. Broadband service helps rural businesses find markets that otherwise might be unavailable to them, facilitates online ordering and billing, and integrates the rural economy with the rest of the country (and the world) more effectively than is possible over slow-speed internet connections. It also allows continued access to online training and education.
Additional Resources on Broadband for
Jobs and Economic Growth
- "Broadband and Business: Leveraging Technology in Iowa to Stimulate Economic Growth". Connect Iowa, May 2011
- “The Digital Divide and Economic Benefits of Broadband Access”. Council of Economic Advisors, March 2016 (PDF)
- “Where The Jobs Are: The App Economy”. Dr. Michael Mandel, South Mountain Economics, LLC. February, 2012. (PDF)
- “The Importance of Broadband to Economic Development: Corporate site selectors consider it a critical piece of infrastructure”. Matt McQuade, Site Selection Magazine. September, 2011. (web page)
- “Municipal Networks and Economic Development”. Institute for Local Self Reliance.
- “Community Broadband Creates Jobs”. Institute for Local Self Reliance.
- "Internet Connectivity and Utilization in Tennessee 2016". Strategic Networks Group, June 2016 (PDF)